Applications
How Data Flows on CFG? How application-specific Data Flows through the Nodes (BB) and Edges (control flows) of CFG (a program)
- may analysis: over-approximation
- must analysis: under-approximation
- input and output statses
- Transfer Function
- forward analysis: $\text{OUT}[s]=f_s(\text{IN}[s])$
- backward analysis: $\text{IN}[s]=f_s(\text{OUT}[s])$
- Control Flow
- $\text{IN}[B]=\bigwedge_{P\text{ a predecessor of }B}\text{OUT}[P]$
- Key
- Domain, Direction, May/Must, Boundary, Initialization, Transfer function, Meet
Reaching Definitions Analysis
- definition of a variable: a statement that assigns to a value
- whether the a definition d is reachable at program point p
- usage
- detect possible undefined variables
- $\text{OUT}[B]=\text{gen}_B\cup(\text{IN}[B]-\text{kill}_B)$
Live Variables Analysis
- whether the value of variable v at program point p could be used along som path in CFG starting at p
- usage
- register allocations
- $\text{OUT}[B]=\bigcup_{\text{S a successor of B}}\text{IN}[B]$
- $\text{IN}[B]=\text{use}_B\cup(\text{OUT}[B]-\text{def}_B)$
Available Expressions Analysis
- whether an expression must be constant at a point
- x op y is available if
- all paths from the entry to p must pass through the evalution of x op y
- after the last evaluation of x op y, there is no redefinition of x or y
- must-analysis
Constant Propagation
- Given a variable $x$ at program point $p$, determine whether $x$ is guaranteed to hold a constant value at $p$
- $\text{OUT}[B]=(x,v)$
- nondistributivity
Lattice
- Partial Order: poset $(P,\subseteq),\subseteq$ is binary relation that defines a partial ordering over $P$, $\subseteq$ has the following properties:
- reflexity: $\forall x\in P,x\subseteq x$
- antisymmetry: $\forall x,y\in P,x\subseteq y\wedge y\subseteq x\Rightarrow x = y$
- transtivity: $\forall x,y,z\in P,x\subseteq y\wedge y\subseteq z\Rightarrow x\subseteq z$
- upper bound $u$: $\forall x\in S, x\subseteq u, S\subseteq P$
- lower bound $1$: $\forall x\in S, 1\subseteq x$
- least upper bound(lub or join) $\cup S\in P$: $\forall u, \cup S\subseteq u$
- two elements: $a\cup b$
- greatest lower bound(glb or meet) $\cap S$: $\forall 1, 1\subseteq\cap S$
- two elements: $a\cap b$
- lub and glb is unique
- lattice: $\forall a,b\exists a\cup b,a\cap b$
- semilattice: $\forall a,b\in P$
- only $a\cup b$ exists, $(P,\subseteq)$ is called a join semilattice
- only $a\cap b$ exists, $(P, \subseteq)$ is called a meet semilattice
- complete lattice: $\forall S\subseteq P,\exists\cup S,\cap S$
- greatest element $\top=\cup P$
- least element $\perp=\cap P$
- Every finite lattice is a complete lattice
- Product Lattice: $L_i=(P_i,\subseteq_i),L^n=(P,\subseteq)$
- $P=P_1\times\cdots\times P_n$
- $(x_1,\cdots, x_n)\subseteq (y_1,\cdots, y_n)\iff (x_1\subseteq y_1)\wedge\cdots\wedge (x_n\subseteq y_n)$
- A product lattice is a lattice
- if a product lattice $L$ is a product of complete lattices, then $L$ is also complete
- monotonicity: $f:L\rightarrow L,\forall x,y\in L,x\subseteq y\Rightarrow f(x)\subseteq f(y)$
- fixed-point theorem: if $f:L\rightarrow L$ is monotonic and $L$ is finite, then the least fixed point of $f$ can be found by iterating $f^k(\perp)$ until a fixed point is reached, greatest fixed point of $f$ can be found by iterating $f^k(\top)$
- height of a lattice $h$: the length of the longest path from Top to Bottom in the lattice
- distributed $F$: $F(x\cup y)=F(x)\cup F(y)$
Foundation
-
Iterative Algorithm (IN/OUT equation system)
- Input: CFG (kill and gen computed for each basic block B)
- Output IN[B] and OUT[B] for each basic block B
- Algorithm
OUT[entry] = {}
for (each basic block B-entry)
OUT[B] = {}
while (changes to any OUT occur)
for (each basic block B-entry){
IN[B] = union_{P a predecessor of B} OUT[P]
OUT[B] = gen_B union (IN[B] - kill_B)
}
- CFG with $k$ nodes: $X_i=(\text{OUT}[n_1],\dots,\text{OUT}[n_k])_i\in V^k,F:V^k\rightarrow V^k$
- $X_{i+1}=F(X_i)$
- fixed point $X_i=X_{i+1}$
- Data Flow Analysis Framework $(D,L,F)$
- $D$: a direction of data flow
- $L$: a lattice including domain of the values $V$ and a meet or join operator
- $F$: a family of transfer functions from $V$ to $V$
- Lattice height $h$, number of nodes $k$, at most $i=hk$ iterations
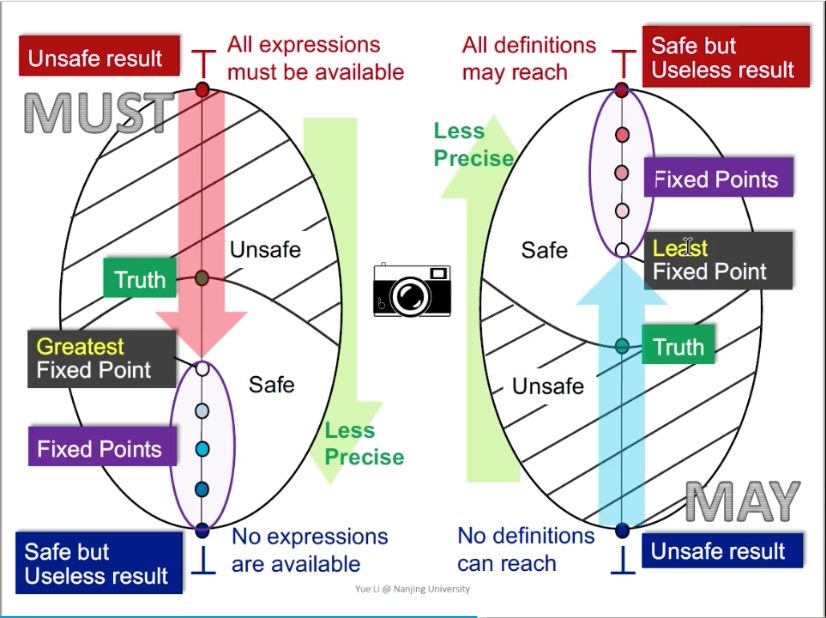
- may analysis
- bottom $\perp$: unsafe = no definitions can reach
- top $\top$: safe but useless result = all definitions may reach
- truth
- least fixed point
- must analysis
- top $\top$: unsafe - all expressions must be available
- bottom $\perp$: safe but useless result - no expressions are availble
- greatest fixed point
- MOP(Meet Over all Paths): $\text{MOP}[s_i]=\cup/\cap_{\text{A path P from Entry to }S_i} F_P(\text{OUT}[\text{Entry}])$
- $F(x)\cup F(y)\subseteq F(x\cup y)$
- MOP $\subseteq$ Ours
- distributive then $=$ (Bit-vecotr or Gen/Kill problem)
- Worklist Algorithm: add successors of changed B to Worklist